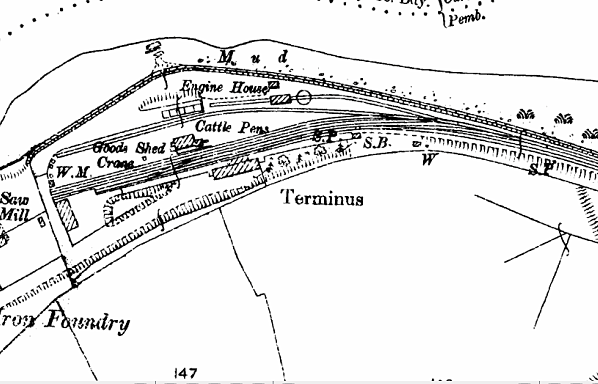
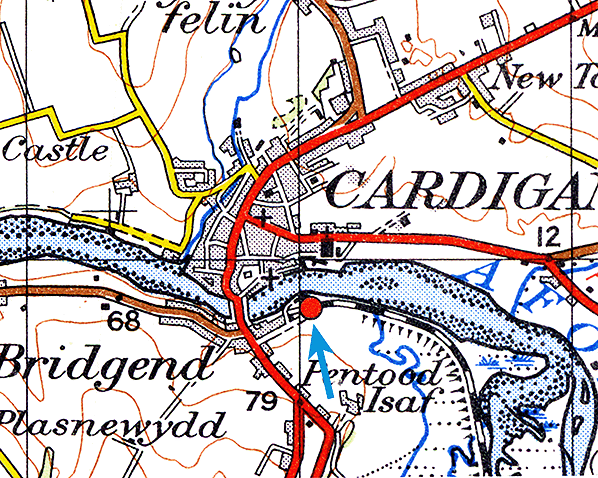
Notes: Cardigan station had a single platform with a single storey station building with a canopy in over the platform and a run round loop. The building included booking office, waiting room and toilets.
A wooden signalbox at the east end of the platform controlled access to the goods yard and engine shed. The goods yard consisted of two additional sidings parallel with the passenger platform running either side of the large stone goods shed. A third siding at the west end of the loop served a cattle dock. Cattle pens were sited on the north side of the yard adjacent to the engine shed and a 5-ton crane was sited at the east end of the goods shed. At a later date a large warehouse was built on the north side of the goods yard.
Cardigan handled a wide variety of goods traffic including, coal and fertilisers and livestock and after closure of the line to passengers the station remained open for goods traffic until 27th May 1963. After that date the station remained open as a non rail connected coal depot until 5th April 1965 with final closure on 6th September 1965. British Railways staff were employed at the station until November 1964, after that date the depot was unstaffed.
The stone engine shed was built in 1885, there was also a water tank and a turntable. Despite the shed being sited alongside the River Teifi there was often a shortage of water and a special tank wagon was available for a number of years when an additional supply of water was required. Cardigan was a sub-shed of Neyland. The shed closed in 1962 when the passenger service was withdrawn.
BRIEF HISTORY OF THE WHITLAND & CARDIGAN RAILWAY
In 1845 there was a proposal to build a branch line from Carmarthen to Cardigan at the mouth of the River Taf as part of the planned Great North and South Wales & Worcester Railway; nothing came of this scheme. In 1854 the Carmarthen and Cardigan Railway was formed with the intention of building a broad gauge line from the South Wales Railway at Carmarthen to Newcastle Emlyn and Cardigan, together with a deep water port at Cardigan. The SWR had opened their line form Chepstow to Swansea in 1850, extending to Carmarthen in 1852 with the intention of eventually reaching Neyland.
 |
Construction started in 1857 and by September 1860 it had reached Conwil Elfed; it took a further four years to reach Llandysul. Due to financial difficulties this was to remain the end of the line for another 31 years before the link to Newcastle Emlyn was completed by the Great Western Railway; but the line, which had been converted to standard gauge in 1872, never |
reached Cardigan.
During the 1860s, mine and quarry owners along the Taf Valley realised that the troubled C & CR would be of little benefit to them even if it did ever reach Cardigan. Their best interests would be served by a line running south from Cardigan along the valley. To achieve this aim, the proprietor of Glogue Slate Quarry spearheaded the promotion of the standard gauge Whitland & Taf Vale Railway, which would provide a better outlet for the slate and minerals of the valley. The proposed line would run from Whitland on the SWR (part of the GWR since 1862) to Crymmych, on the main road between Cardigan and Haverfordwest. Engineer James W Szlumper was employed to draw up plans for the line ready to put before Parliament.
There was a lot of local support for the line, and the promoters had little difficulty raising sufficient capital. At this time the SWR was still broad gauge so, to enable trains to run into Whitland, the new company had to negotiate with the GWR to lay mixed gauge track to its junction with the W & TVR, 2’/4 miles west of Whitland.
 |
The Whitland and Taff Vale Railway Bill was unopposed and was passed by Parliament in 1869, and in the spring of 1870 the company started negotiation to acquire the necessary land. Much of this was owned by the church, and some of the landowners were making such exorbitant demands that the project was almost abandoned. Eventually agreements were reached and a contractor, Edward Lewis, was appointed on 13th October 1870. Lewis undertook to build the single-track 14¼ railway to James Szlumper's specification for £8,700.
Construction started on 8th November 1870 and, despite bad weather, there was rapid progress. Five miles of earthworks had been completed by February 1871, and it was anticipated that mineral traffic to Glogue would be possible by 1st May that year, and to Crymmych by the summer assuming that the GWR completed the junction with their line; this didn't happen until June 1871.
By now the company was in financial difficulty and raised further capital by offering unsold shares at a reduced rate to existing shareholders, with any remaining shares being offered to the public. Work then proceeded steadily, and by August 1872 the line was ballasted from the junction to Llanglydwen .It was anticipated that on completion of ballasting to Glogue six or eight weeks later the permanent way would be ready for light traffic. The company was hopeful that the line would be ready for heavy goods traffic by November that year, and the rolling stock was ordered and staff appointed. |
Completion of the line was further delayed due to deliberate vandalism and a dispute with the GWR over delivery of rails and fishplates, and once again the company was in financial difficulties with payments to the contractor being in arrears. At a board meeting on 11th February 1873, Edward Lewis, was asked to hand over the line, including the sections that were unfinished; he eventually complied, and on 1st March 1873, although the arrears had still not been cleared, work restarted.
The junction was examined by the Board of Trade on 15th March. Once a few improvements had been made the line was officially opened for goods and mineral traffic on 24 March 1873, with two daily trains between Whitland and Glogue quarries calling at all intermediate stations: Llanfalteg, Login, Llanglydwen, Rhydowen and Llanfyrnach.
Following the departure of Edward Lewis - who had to resort to legal action to get at least some of his money - the company was forced to take on the remaining work itself, employing the existing workforce to complete the line to Crymmych, which opened to goods traffic in July 1874. Steady progress was made to bring the line up to the standard required to carry passengers, and on 29th May 1875 the Board of Trade was notified that the line would be ready for final inspection two weeks later. An inspector was appointed, but he failed to turn up within the ten day period provided by statute. Having received no communication from the Board of Trade, the line opened to passenger traffic on 12th July 1875 without an inspection.
Initially there were four down trains (northbound) and three up trains a day with a journey time between Whitland and Crymmych Arms (the station at Crymmych was always known as Crymmych Arms) of between 1 hour 10 minutes and 1 hour 30 minutes. A connecting road service to Cardigan met two of the trains.
| The line was eventually inspected three days later, and the company was informed that it must suspend the passenger service for one month to allow the required modifications to be carried out. The directors ignored this directive, stating that it had acted within the law as the inspector had failed to turn up within the specified period, and that once a line had been opened the |
 |
Board of Trade had powers only to recommend works and not to compel them. .
Early traffic receipts were encouraging with a dividend of 3% on ordinary shares in the second half of 1875.
In 1876 James Szlumper drew up plans for extending the line to Cardigan, and, after some initial caution, the directors agreed to seek parliamentary approval. The Whitland & Taf Vale (Cardigan Extension) Railway Act was passed in 1877, and the company then became known as the Whitland & Cardigan Railway. At this time the directors were aware that eventually their line would probably become part of the GWR.
Although reluctant to start work until sufficient finance was available, the board could not resist an offer of cheap rails, and on 22nd April 1878 they agreed to start work immediately at both ends.
 |
Due to difficulties buying all the land work did not in fact start until August that year. Progress was slow following disagreements between Szlumper and the company; eventually all construction stopped, and Szlumper was dismissed. A new engineer, J B Walton, was appointed, and limited work on the extension restarted, but serious financial difficulties inhibited progress, and the company entered into negotiations with the GWR to take over the running of the line. After protracted negotiations the GWR agreed to work the line for 70% of receipts in the first year, and a new Bill was put before Parliament in August that year to facilitate the agreement between the two companies and authorise a new route between Boncath and Cilgerran. In 1878 it was decided to relay the entire line with a heavier rail, and the GWR agreed to contribute towards the cost of this; by now take over by the GWR was generally expected.
Once purchase of the necessary land had been completed, construction of the Cardigan extension began in earnest on 1 May 1883 and went ahead rapidly. The permanent way from Crymmych to Boncath was completed in August 1884 reaching Cardigan a year later. No authority had been granted to run a passenger service, but a special excursion from Cardigan to Tenby was arranged, with the first passenger train running in and out of Cardigan on 10th August 1885, although the opening of the extension was still over a year away.

By the end of 1885 take-over of W & CR. services by the GWR on the completion of the Cardigan Extension Railway was believed to be imminent. There was local outrage when the GWR announced that the stations at Login, Rhydowen and Glogue would close to passenger traffic within a year of taking over the line, if passenger receipts did not improve.
 |
In July 1886 notice was given to the Board of Trade that the Cardigan Extension was ready for inspection. This took place on 29/30 June despite the fact that there was still unfinished work at Cardigan station. Inevitably the inspector postponed the opening of the line for one calendar month from 6 July to allow this work to be completed. The GWR agreed to operate |
the line from 1st September 1886. The station in fact opened on 31st August 1886; this was only the second time the W & CR operated the service into Cardigan, which was handed over to the GWR that evening. Additional intermediate stations were opened at Boncath and Kilgerran. Although the extension was already open the official opening ceremony was held the following day. Under the 1883 agreement all existing rolling stock was handed over to the GWR.
By this time, both passenger and goods traffic was in decline. Although the Glogue quarries were still profitable, agricultural traffic - which was the main business of the line - was in decline. There had been a disastrous slump in lead prices between 1876 and 1885, and Llanfyrnach mine closed in 1890. Glogue Quarry remained in operation until March 1926, when it too closed.
It came as no surprised when the W & CR was finally absorbed into the Great Western Railway with effect from 1st July 1890. The earlier threat of station closures was never carried out, and all stations remained open until final closure of the line. For the next 70 years the line settled down to a quiet and eventless existence.
Crymmych developed as one of the important agricultural centres of west Wales and was the busiest intermediate station on the branch. A 'Cattle Special' ran from Carmarthen Junction to Crymmych on the last Tuesday of each month to serve the cattle, horse and sheep fair. There was also a good trade in rabbits from stations on the line.
| The GWR maintained a freight service of two trains a day in each direction on weekdays, and one each way on Saturdays. In the war years extra trains were run, but on an ‘as required’ basis. The railway was generally busy. Crymmych handled large quantities agricultural machinery, animal foodstuffs and coal, and every Monday a consignment of beer was received |
 |
from Burton-on-Trent. At Cardigan the sidings were often crowded to capacity, especially with coal wagons and vans of fertilisers. Even if the passenger trains were not full local people felt that the freight was enough to make the railway profitable, which was probably true before WW2.
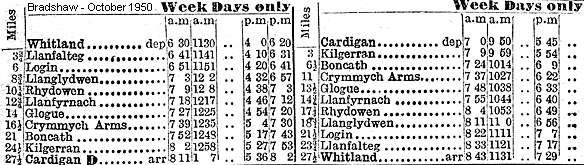
On 1 January 1948, the Cardigan branch of the GWR. became part of the Western Region of the nationalised British Railways. In the period of BR ownership the passenger service consisted of four down and three up trains. The trains called at all the intermediate stations; latterly Llanfalteg, Login, Rhydowen, Glogue and Kilgerran were downgraded to 'halts'. Of these only Kilgerran became unstaffed; at the rest at least one person was required to deal with level crossing gates.
Post war freight traffic was almost as varied as ever. Coal and fertilisers were conveyed to Llanfyrnach, Crymmych and Cardigan. At Kilgerran and Boncath the business was largely timber, and at Llanglydwen it was coal. A lot of milk went by rail, and although there was some decline in cattle traffic even in the late 1950s, plenty of cattle wagons were to be seen at Crymmych. In spite of this volume of goods traffic, and some steady custom in passengers from villages devoid of any other public transport, it became obvious in the 1950s that the days of the railway were numbered as the popularity of the car increased.
Cardigan was still quite a popular destination for tourists in the summer months, but this generated insufficient traffic to make the passenger service viable along the steep and winding line, which took its toll on the locomotives and rolling stock. The line had a remarkable number of tight curves along its route - few branches in Britain could match it and progress along the branch was always slow. In 1961 the first passenger train of the day from Whitland to Cardigan managed a breathtaking average speed of about15 mph. There were seven level crossings, all of which had to be manned, and signalmen or goods yard staff were needed at Llanglydwen, Crymmych, Boncath and Cardigan. It therefore came as no surprise when, in February 1962, British Railways submitted proposals for the closure of the line to the Transport Users’ Consultative Committee. There was little opposition, and closure was approved: passenger services were withdrawn on 8th September 1962, at the end of the summer timetable.
In the weeks up to closure the line was busy and on the last day there was a large crowd eager to travel on the final train, including one passenger who had been on the first official train into Cardigan in 1886. About 500 passengers were crammed into the last service out of Cardigan. A new bus service started the following Monday, calling at all the intermediate stations. Even this unprofitable and was withdrawn after three years.
The line remained open for freight traffic with a reduced service of one train in each direction on a Monday and two trains Tuesday - Friday. Cardigan shed was closed, and the halts at Llanfalteg, Login and Rhydowen were closed completely with trains only stopping at Glogue to take on water. Parcels traffic was also withdrawn from Llanglydwen, Llanfyrnach and Boncath.
Most of the staff were retained at Crymmych and Cardigan, but this was to be short-lived as the freight service was withdrawn completely from 27th May 1963. One or two trains ran over the line after that date to collect materials and to clear wagons. The last man employed on the line by British Railways left Cardigan in November 1964. Track lifting operations began in December 1963 and were completed by July 1964. Through the 1960s the land was disposed of, mostly to local farmers or other adjoining landowners.
Sources: The Whitland & Cardigan Railway by M R C Price published by the Oakwood Press 1976 and 1986 ISBN 978-0853614098
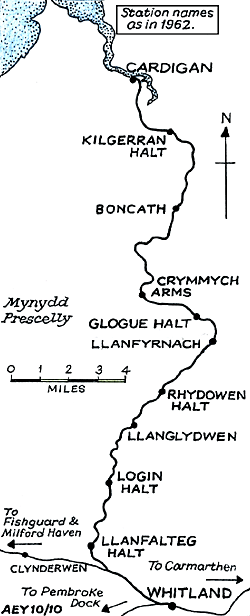
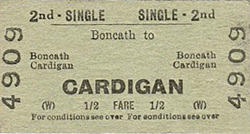
Tickets from Michael Stewart, route map drawn by Alan Young,
Click here for a collection of pdf files about the Cardigan branch held by Ceredigion County Council. Many are newspaper cuttings about the construction of the line.
To see other stations on the Whitland & Cardigan Railway click on the station name: Whitland, Llanfalteg, Login, Llanglydwen, Rhydowen, Llanfyrnach,
Glogue, Crymmych Arms, Boncath & Kilgerran |

old11.jpg)
old3.jpg)
old12.jpg)
2.jpg)
9.jpg)
9.jpg)
7.jpg)
12.jpg)
16.jpg)







old10.jpg)

 Home Page
Home Page