Notes: In November 1862 the LNWR introduced services from Camden and Harrow along the West London Railway to the old terminus at Kensington. When the West London Railway fully reopened along with the West London Extension Railway on 1st April 1863 a third Kensington Station was under construction north of the second site but initially the second station was retained for this service until the new station was ready for use.
 |
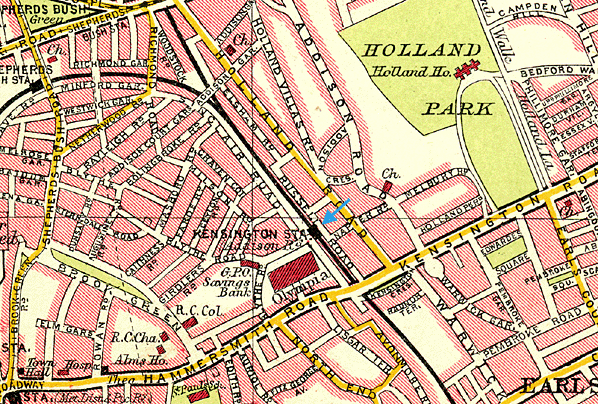
The new station was to have been built on the south side of Hammersmith Road with long platforms stretching from Hammersmith Road to Brompton Road with access from both roads. Eventually a site a little to the north of the existing Kensington station was selected. Initially only the east side of the station was built as a long through platform and two tracks with a |
'scissors crossing' half way along allowing two trains to use opposite ends of the platform at the same time. On the west side there were a second pair of tracks and a similar scissors crossover but this was later removed. On the east side of the platform there were three lines serving two terminal bay platforms to the north of the station building and two further bay platforms to the south..
| The through lines and the north bay platforms were laid with mixed gauge track while the south bay had only standard gauge track. The weatherboarded station building comprised booking hall, waiting rooms, stationmaster's office, parcels office and a refreshment room. It had a forecourt with a covered entrance for carriages and cabs. There was a substantial 'ridge and |
 |
furrow' style canopy over the central part of the platform and round the end of the building. The bay platforms were left open.
There was no entrance on the west side of the station which at that time was open countryside (before Olympia was built) occupied by the Royal Vineyard Nursery.
 |
The east or 'up' side of the station was ready for use in 1864 and trains were diverted there from the earlier station on 1st July 1864. With the opening of the new station, the GWR introduced a terminating service from the Metropolitan line from Moorgate using a spur from Latimer Road which joined the West London line north of Shepherds Bush, terminating at the north west bay |
platforms. This service started on 18th July 1864 but was short lived running for four years on broad gauge track and a further year on standard gauge track before being withdrawn.
A second 1100 foot long platform was added on the west or 'down' side in 1868 to ease overcrowding with a second booking office provided in 1871. The building on this side was smaller but was protected by a similar length and design canopy with a footbridge linking the two platforms. A bay platform was added to the north side of the new platform for use by the LSWR when their service arrived from Richmond on 1st January 1869. A siding was added to the south of the station. There was intended to be another bay platform here and although the earthworks were started the platform wasn't built for another 80 years.
When Kensington High Street Station was opened on 1st October 1868 the station was renamed Kensington Addison Road to avoid confusion with the new station.
In 1930 the footbridge was replaced by a new bridge a little further south. Not only did the new bridge cross the four tracks but it was also extended into the exhibition building at Olympia. The old footbridge remained in use until it was demolished during WW2.
| During September/October 1940 Addison Road station was hit by bombs four times receiving its worst damage on the night of 21/22 October which wrecked the buildings on the east side of the station and damaged most of the canopies. As a result, the station was closed to local passenger traffic along with the entire West London Line although a workers shuttle |
 |
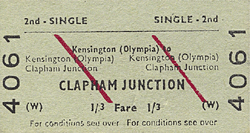
service to Clapham Junction was maintained throughout the war. The line remained open for freight traffic including much war-related traffic and Addison Road was used as one of the main clearing stations for evacuation trains.
At the end of the war, Addison Road was battered and roofless and with the impending threat of nationalisation there was no money available for repairs and improvements and the through service between Willesden & Clapham Junction was not reintroduced. Only the District line service from Earls Court was reinstated on 19th December 1946 when the station was renamed Kensington Olympia but this only ran when there was an exhibition at Olympia. Initially these trains used the south end of the 'up' platform but as this meant crossing the line to reach Olympia so the south west bay was finally completed and brought into use on 3rd March 1958. The workers peak hour shuttle to Clapham Junction also continued to run.
 |
By the 1960's all the old platform buildings had been cleared away and on 24th May 1966 a Motorail terminal opened on the site of the north west bay platforms with car-transport services to a wide range of destinations in Scotland, Wales and the West Country. By 1981 the number of cars using the Motorail terminal had dwindled and with little chance |
of improvement motorail facilities were discontinued at the end of the summer season and the terminal closed..
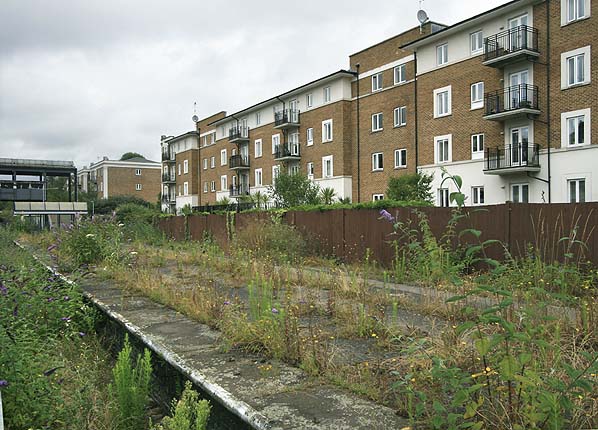
In 1983 all the bay platforms on the west side of the station were taken out of use and the track was lifted and the bays were filled between the platform edges. The site was then used as an additional car park for Olympia. At the same time the 'up' platform was cut at both ends and the track relaid as a siding with buffers at the north end with all station facilities being concentrated on the west side of the line. At the same time the crossings were removed allowing higher train speeds on the through lines.
| This marked a low point in the history of the station. In 1986 the District Line recommenced a full service, joined in 1994 by a rejuvenated service on the West London Line, from Willesden Junction to Clapham Junction and from Watford Junction to Brighton. To accommodate this, a new shorter platform was built on the west side of the line. |
 |
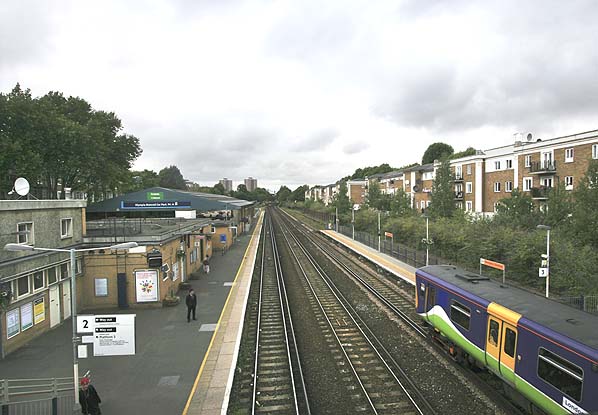
Today the station is relatively quiet compared to its busy past. A large number of freight trains pass through the station, as the West London Line is the main freight route from north of London to the south-east of England and the Channel Tunnel.
 |
Prior to the transfer of Eurostar services to St Pancras International in November 2007, Eurostar trains passed through on their way from Waterloo International to North Pole depot. The link to the Great Western Main Line (at North Pole Junction, three miles to the north), avoiding the western central London terminus of Paddington station, meant that the |
station was to play an important role in the Cold War should a nuclear exchange have seemed likely. The station was part of the secret plans to evacuate large numbers of civil servants to the Central Government War Headquarters underground nuclear bunker at Corsham in Wiltshire during the period leading up to a nuclear war.
Kensington Olympia was also a backup terminus for the Eurostar services in the event that Waterloo International became unusable in an emergency. Until the move to St Pancras, immigration facilities were maintained at Kensington Olympia for this purpose and possibly also because of the aborted plan to run Eurostar services from regional stations in the UK through to the continent.
BRIEF HISTORY OF THE WEST LONDON LINE
As part of a general improvement of transport in West London, the Kensington Canal was opened on the 12th August 1828 running north from the Thames at Chelsea to a basin near Kensington.
| During the 1830's, the impending establishment of the London and Birmingham Railway (in 1833) and of the Great Western Railway (in 1835) was causing uncertainty about the future development of communications throughout west London. Neither company had yet decided upon the site for its permanent London terminus. But even before their |
 |
incorporation as a company the directors of the Great Western Railway had in 1834 considered building a goods terminus beside the Kensington Canal basin, giving them access by water to the London docks.
The Birmingham, Bristol & Thames Junction Railway was authorised by an Act of Parliament of June 1836 with powers to buy the canal and to build a railway northward to the London and Birmingham Railway at Willesden across the proposed route of the Great Western which opened to Bristol in 1838; thus creating a through route mainly for freight traffic from Bristol and Birmingham to the River Thames, the capital's main commercial artery. The directors of the new company expected the Great Western and the London & Birmingham to use their proposed new line as the most convenient route to the Thames. They also hoped the line would generate passenger revenue from the L & B and GWR if it was extended from their proposed southern terminus at Kensington to a new terminus near Hyde Park Corner, the gateway to London.
 |
Construction started in 1836 with Sir William Hosking as engineer. The new line left the London & Birmingham Line at Willesden running south across the Great Western on the level where an interchange station was to be built with platforms on both lines. A further station was to be provided at Shepherds Bush before the line reached its southern passenger |
terminus at Kensington from where it passed under Hammersmith Road to a goods yard adjacent to the Kensington canal basin near Warwick Road.
Having purchased the ailing Kensington Canal Company for £36,000 the new company was itself in financial difficulty and a second Act of Parliament was required in 1840 to raise extra capital; at this time the company's name was shortened to the West London Railway. Trials to show-off the potential of the atmospheric railway system were held from 1840 to 1843 on a half-mile section of track adjacent to Wormwood Scrubs, leased to the system's promoters; but in the event, the line proceeded with conventional power.
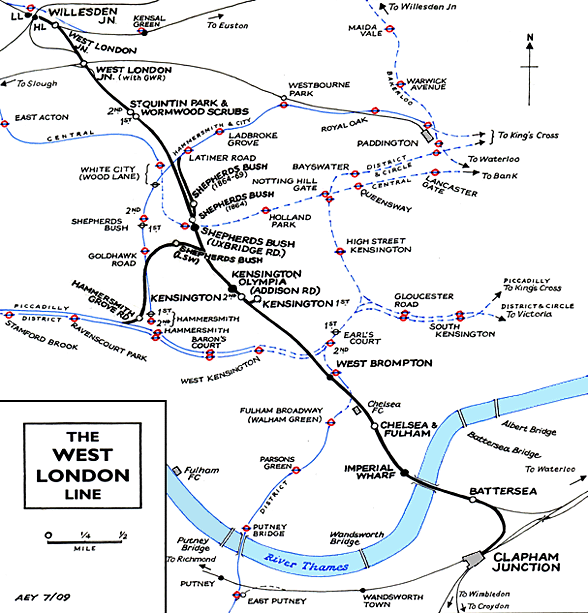
The 2.5 mile single line officially opened between West London Junction, Willesden and Kensington on 27 May, 1844, with regular passenger services beginning on 10 June with a 30-minute interval service. By this time the L & B and GWR had chosen their London termini and were no longer interested in using the West London Railway. The terminus at Kensington was some distance from Kensington itself and any potential commuters, and the line ran through open country throughout; from the outset it was not a commercial success.
It is said that the first train had one passenger with little improvement in the following months. In September and October 1844 passenger receipts were only £15 10s per month and according to the company minutes of 25th October 1844 "The 5.55pm from Kensington was delayed so long at the crossing that it didn't reach West London Junction until 7pm and the solitary passenger had missed the last train to Harrow." The minimal level of passenger returns became such a regular target of Punch magazine that the line started being called Punch's Railway "leading from nowhere to nowhere". The company blamed the failure of the line on the refusal of the L & B and GWR to stop their to stop their long distance trains at the respective junctions with the West London and with losses of £50 per week the line was forced to close after the last train on 30 November 1844 after less than six months.
| An Act of 1845 authorised the Great Western and the London and Birmingham to take out a joint lease of the West London Railway in 1846 but passenger services were not restarted and the line was only used to carry coal. On 31st July 1854 the company was vested jointly in the London & North Western Railway and the Great Western Railway. The rubbish-strewn |
 |
Kensington Canal was soon to prove a millstone with the company’s single locomotive often having to cope with foul flood water at high tide. Following an outbreak of cholera caused by the stagnant water, a further Act in 1859 allowed the companies to fill in the canal from the Kensington basin as far south as the bridge under the Kings Road and to construct the West London Extension Joint Railway which was formed by Act of Parliament on 15th August 1859 to meet the lines south of the river to a junction with the London & South Western Railway and the London Brighton & South Coast Railway at Clapham Junction. The WLER was a joint venture between the LNWR, GWR, LSWR and LBSCR with the latter two companies holding one third of the capital between them.
 |
Another source of problems for the line was the flat junction with the Great Western south of Willesden with a number of serious collisions taking place at the level crossing. This was eventually overcome by realigning the West London Line over the Great Western to the west of the crossing; this was brought into use in October 1860. |
The northern end of the Kensington Canal was infilled in 1861 with much of its course being used for the WLER. The new double track line between Willesden and Clapham Junction opened to passenger traffic on 2 March 1863. Kensington & Shepherds Bush (renamed Uxbridge Road) stations were rebuilt a little to the south of the original sites with new stations provided at Chelsea and Battersea and a further station opening at West Brompton on 1st September 1866. A third rail was laid to allow broad gauge trains to use the extension but this had limited use with broad gauge passenger trains running into Victoria until October 1866 and freight trains running to Chelsea Basin until November 1875.
Unlike its predecessor, the West London Joint Railway as it became known, was an immediate success. A spur from the Hammersmith & City line at Latimer Road opened on the 13th July 1864 which gave Great Western trains direct access to the line from the London direction. On 1st January 1869, the London & South Western Railway opened a line from Richmond to a junction with the West London line just north of Kensington Station and on the 12th April 1869 a connection between the West London Line and the District Railway was made at West Brompton and a northbound spur from the District Railway to Kensington was opened on 1st February 1872. There was also a connection to the District Railways Lillie Bridge Depot. On 1st June 1877 the District Railway was extended a short distance west from its station at Hammersmith to a junction with the 1869 LSWR's Richmond Branch.
The new multiplicity of connections led to considerable development of transfer freight traffic between the northern and southern lines while the former also opened depots south of the river. In spite of the equivalent possibilities for through passenger traffic, this didn't begin until 1904 and never attracted the expected passenger revenue.
| The first section of the West London Line to be electrified was between the Latimer Road spur and Kensington in 1909 allowing Metropolitan trains to reach Kensington. Further electrification took place in 1914 when LNWR trains ran into Earls Court. On 16th April 1917 the GWR opened a link between its Birmingham line and the North London line at North |
 |
Acton although this was used mainly for freight traffic.
During the 1923 Grouping the West London Railway nominally retained its independence although the West London Extension Railway was absorbed.
Despite the early heavy passenger numbers use of the line dwindled with the construction of the deep-level underground network and the introduction of trams and motor busses which provided a quicker and more convenient route for commuters to reach central London. Local north-south passengers also deserted the line in favour of road transport. WW2 hastened the demise of the now uneconomic passenger services. Following severe bomb damage, the advertised steam services from Clapham Junction - Kensington ceased on 20th October 1940 and the electric services, LMSR from Willesden and LT now from Edgware Road on 3rd and 20th October respectively.
 |
The line remained in service as an important freight link. After the war only the short section of line between Kensington and Earls Court was reopened for passenger traffic with the service being provided by London Transport’s District Line from 19th December 1946, but only when there was an exhibition at Olympia. A workmen's diesel hauled passenger |
service ran between Clapham Junction and Kensington with two trains in the morning rush hour and two in the evening. This service received little promotion and most people were unaware of its existence. Most of the conductor rails between Kensington and Willesden were removed between 1946 - 1952.
The line remained busy with 30 freight trains in each direction daily and holiday excursions and special cross country workings were common. On 24th May 1966 the West London Line received a new lease of life with the opening of the Motorail terminal at Kensington, with car-transport services to a wide range of destinations in Scotland, Wales and the West Country. These services ceased in 1988 and the Motorail terminal closed. It’s now used as a covered car-park and the reception area is now the booking hall and ticket office.
| Despite this set back for the line, a renaissance began in 1986 when the District Line recommenced a full service, joined in 1994 by a rejuvenated service on the West London Line, from Willesden Junction to Clapham Junction and from Watford Junction to Brighton. A new station was opened at West Brompton on the site of the original station on 30th |
 |
May 1999. A further new station at Shepherds Bush opened on the site of the former Uxbridge Road Station on 28th September 2008 and a third new station called Imperial Wharf on a new site between the old Chelsea & Fulham and Battersea stations is currently under construction and is due to open in late 2009.
The line is electrified at 750 V DC third rail from the south to the North Pole depot, where the electrification changes to 25 kV AC overhead. The work was carried out as part of Channel Tunnel infrastructure improvements in 1993.
 |
Local trains run every half hour and are operated by London Overground. Hourly Southern trains run between East Croydon (formerly Brighton) and Milton Keynes (previously Watford Junction), not stopping at Willesden Junction. The twice daily cross country services from Brighton to Birmingham New |
Street via Reading was discontinued in December 2008.
The line still carries considerable freight traffic and was used by Eurostar trains between Waterloo International and the depot at North Pole Junction prior to November 2007. Recent timetable changes have meant that some London Overground peak hour trains now continue beyond Willesden Junction onto the North London Line to Stratford.
Tickets from Michael Stewart except 5439, 4061 & 17542 Brian Halford
Bradshaw from Chris Hind
Sources:
Click on the station name to see other stations on the West London Line:
Clapham Junction STILL OPEN, Battersea, Imperial Wharf NEW STATION, Chelsea & Fulham, West Brompton REOPENED, Kensington (1st site), Kensington (2nd site), Uxbridge Road REOPENED AS SHEPHERDS BUSH 3rd SITE, Shepherds Bush (1st site), Shepherds Bush (2nd site), St. Quintin Park & Wormwood Scrubbs (1st site), St. Quintin Park & Wormwood Scrubbs (2nd site), West London Junction (1),
West London Junction (2), Willesden Junction STILL OPEN
See also Hammersmith (Grove Road) & Shepherds Bush on the
Richmond - Kensington line |

old6.jpg)
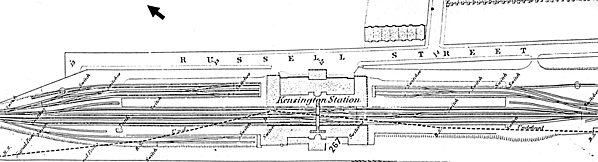 Kensington Station layout in 1867
Kensington Station layout in 1867old3.jpg)
old8.jpg)
road_old12.jpg)
olympia40.jpg)
olympia1.jpg)
olympia3.jpg)
olympia7.jpg)
olympia8.jpg)
















road_old15.jpg)


 Home Page
Home Page