|
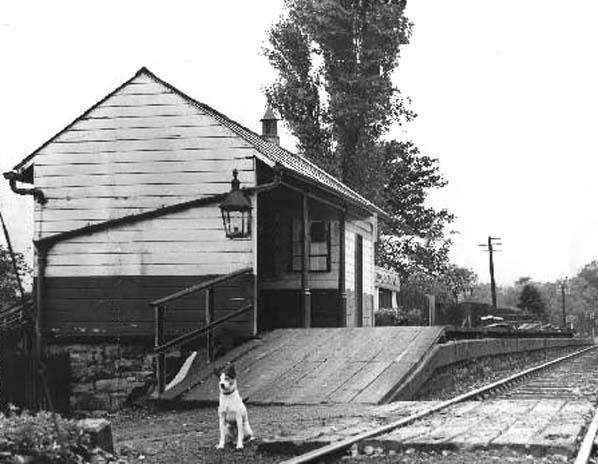
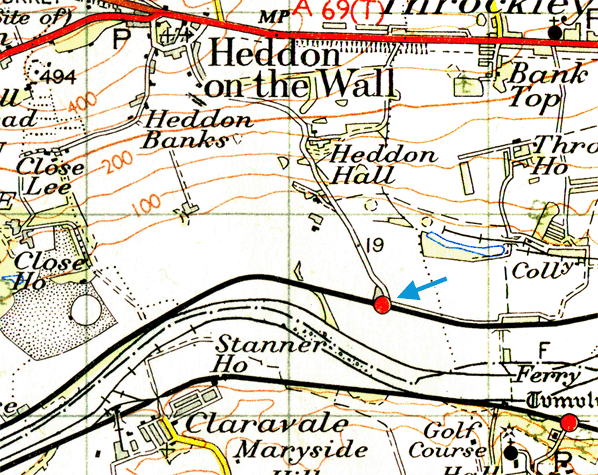
Notes:This delightfully named station was added some five years after the opening of the line. The two 100yd platforms were staggered either side of a level crossing. The buildings were close to the crossing. The up platform (east of the crossing) had two adjoining wooden buildings, both typical of the then current NER style. The smaller western building was a waiting shed; the larger one contained the booking office and a further waiting room. There was a third waiting shed on the down platform. Lemington Colliery waggonway, north of the running lines, had to be slewed northwards to accommodate the up platform. In the vicinity of the station were Heddon Colliery and firebrick works, Bank Farm, and Sir John Jackson’s sidings.
Although used by colliery workers, the valley-floor station was extremely inconvenient for the village, over a mile away up a steep track (Station Road), and being on the north bank of the Tyne, with no bridge, there were no passengers from south of the railway. In 1911, 14,124 tickets were issued, but only 2,428 in 1951; by the 1950s many of Heddon’s residents were probably unaware that there was a station! After closure the station was demolished by 1963.
William Harle was station master from 1898 – 1906. It has been said that he planted 13 trees at the station, one for each of his children. The 1910 photo (below) does show a regular line of trees behind the boundary fence.
(There are rumours that a railwayana collector has a British Railways Heddon-on-the-Wall totem in his possession. As far as I am aware no totems were fitted at the station. Such a specimen would be extremely valuable!)
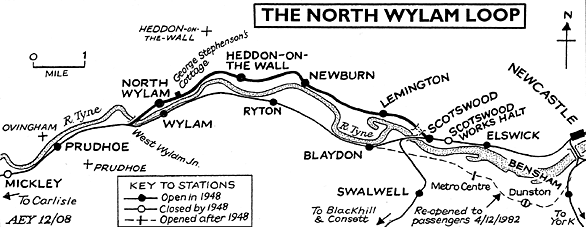
BRIEF HISTORY OF THE SCOTSWOOD TO PRUDHOE LINE, VIA NORTH WYLAM (‘NORTH WYLAM LOOP’ or ‘NORTH WYLAM BRANCH’)
 |
The Newcastle-Carlisle route, which opened in 1839, left inhabitants of Newburn and Lemington, north of the river, dependent upon Scotswood station. Although collieries in that area had waggonway access to the Tyne, a rail link was desirable for this traffic. On 16 June 1871 the Scotswood, Newburn & Wylam Railway & Dock Company Bill was successfully |
presented to Parliament, and the line opened from Scotswood to Newburn, with an intermediate station at Lemington, on 12 July 1875. The remainder opened as far as North Wylam station on 13 May 1876 then onward across Wylam Bridge to meet the route via Blaydon at West Wylam Junction in October 1876. Part of the 6½ mile route followed the course of the Wylam Waggonway. This section passed the cottage where George Stephenson was born; the proximity of this waggonway to his childhood home undoubtedly inspired his pioneering interest in railways.
Each end of the new line offered engineering challenges. At Scotswood, a ridge was to be crossed in a cutting, but owing to geological difficulties, a short tunnel was excavated instead. At the west end, the River Tyne was crossed by the graceful Wylam Bridge. Closely resembling Newcastle’s Tyne Bridge, built 52 years later, Wylam Bridge was of wrought iron and had an 80yd arch from which the bridge floor was suspended on vertical ties. The dock in the company’s title was never built because the River Tyne was too shallow and was not dredged as far upstream as Scotswood. Despite being a loop line, passenger trains from Newcastle generally terminated at North Wylam, a practice that continued until the 1950s. In 1889 a complaint by a passenger, whose journey from Heddon involved a transfer with luggage between Wylam’s stations (about a quarter of a mile) to reach Prudhoe or stations west, failed to impress NER officials.
 |
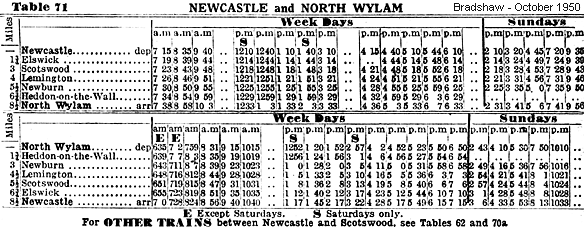
The working timetable of winter 1898-9 shows six passenger trains each way between Newcastle and North Wylam (terminus) at irregular intervals, with an extra market train on Tuesdays and Saturdays leaving Newcastle at 7:55 pm and North Wylam at 8:39 to return to Newcastle, and a Thursday-only 10:35 pm departure from Newcastle to North Wylam. A workmen’s train (Saturdays only) left Newburn at 12:25 pm for Newcastle. The two further passenger workings were Saturday relief trains from North Wylam (dep 1:25 pm) to Newcastle and a 7:40 pm (alternate Saturdays) in the opposite direction. Goods train workings were also apparently confined to the section east of North Wylam, although an express meat train leaving Carlisle London Rd at 4:55 pm was routed along the loop. Otherwise the Wylam Bridge presumably carried only mineral trains.
In 1920 ten trains operated each way on weekdays between Newcastle and North Wylam. By winter 1937-8 the service had strengthened to approximately half-hourly trains on weekdays and hourly on Sundays: some weekday, and all Sunday trains, did not call at Heddon-on-the-Wall. Eventually, in 1955, British Railways promoted the loop to ‘through status’, with several passenger workings daily over Wylam Bridge. For many years, some trains (passenger and freight) actually used this route because it quadrupled the congested Prudhoe-Scotswood section. The 1955-68 passenger trains on the route were at irregular intervals. Sunday trains used the North Wylam loop in its final months, rather than calling at Blaydon and Wylam.
| In 1958 British Railways took the apparently illogical step of closing Lemington, Newburn, and Heddon-on-the-Wall stations (which had no alternative station to use) yet retaining North Wylam, under five minutes’ walk from Wylam on the main Newcastle – Carlisle line. However 1951 traffic statistics show that North Wylam was the busiest of the four stations on the loop: |
 |
37,197 tickets were issued there, but less than 25,000 for the other three stations combined. At that time, moreover, North Wylam was effectively a terminus with negligible traffic to or from the west. Its bookings exceeded those at Wylam (30,261). Beeching (1963) recommended closure of thirteen Newcastle-Carlisle passenger stations including Scotswood and North Wylam, but (according to Map 9 in the report) ‘stopping’ passenger services would continue to use the North Wylam loop – with no station remaining to stop at! - whilst ‘stopping’services would cease to use the route via Blaydon, and Wylam and Blaydon stations would close.
wall_old3.jpg) Station garden in September 1947
Station garden in September 1947 |
The Transport Users’ Consultative Committee Report published on 18 February 1966 addressed BR’s proposal to close Elswick, Scotswood, Blaydon, Wylam, Fourstones, Bardon Mill, Greenhead, Gilsland, Heads Nook, and Wetheral. B.R claimed that these closures would allow accelerated DMU services –making them more attractive to the majority of users- and increase the DMU fleet’s productivity by integrating these ‘express’ services with Newcastle-Hexham local workings. |
North Wylam station was to remain open, and the Blaydon route would close. B.R. explained this decision, noting the expense of maintaining Scotswood Bridge;‘certain advantages’ of the North Wylam route for freight working; declining business at Blaydon; and the ease of transferring Wylam’s business 300yd to North Wylam. B.R. considered the retained stations ‘fairly well placed strategically to attract people to use their cars to the stations and go forward on fast trains to their destinations’.
Trains between Scotswood and Prudhoe via Wylam were suspended from 3 September 1966 for engineering work. They never again stopped at Scotswood’s south platforms. The North Wylam loop platforms remained as the notional railhead for the temporarily-closed Blaydon station, beyond the expected closure date in early January. Scotswood eventually closed in May 1967, when services via Blaydon were restored.
 |
Because BR’s proposal in 1966 to close Wylam but retain North Wylam was rejected, proceedings began in 1967 to close the North Wylam loop. North Wylam station was profitable, with annual passenger receipts of £4,650 against operating costs of £2,100, but abandonment from North Stella (Newburn) to West Wylam Junction, including the bridge over the River Tyne, would save an estimated £8,500 in maintenance and renewal. Whereas BR emphasised the operating advantages of the North Wylam loop a year earlier, now, remarkably, its disadvantages emerged: North Wylam had speed restrictions owing to ‘sharp curves, gradients, and poor foundations’ (maximum gradient was a very short stretch at 1 in 85) and would be expensive to upgrade to trunk route standards!
 |
Valiant protesters, including Northumberland County Council, opposed the closure. Grounds for objection included the proximity of North Wylam station to a planned housing estate; the unpleasant walk over the bridge to Wylam station in inclement weather; and the inconvenient layout and poor condition of that station. However, closure was inevitable. The TUCC report |
of 12 September 1967 concluded that Wylam (population 1,495) did not warrant two stations, and that passengers used either station ‘according to which particular train suited their immediate requirements’.
On 11 March 1968 passenger traffic ceased on the loop and North Wylam closed. I travelled on two of the trains on Saturday 9 March (the penultimate day of service). There was a sense of ‘business as normal’ – no signs of impending doom, or special events as were seen on some other lines immediately prior to closure. Rails through North Wylam were retained until April 1972, when the line was cut back to Newburn. The Scotswood-Newburn section was taken out of use in December 1986. Most of the loop is now a cycle route and footpath (Tyne Riverside Country Park) with Stephenson’s Cottage as an enduring feature of interest.
Tickets from Michael Stewart
Sources:
- Railways in Northumberland by Alan Young (Pub: Martin Bairstow 2003) from which this article is adapted.
- The Railways of Northumberland and Newcastle upon Tyne by J. A Wells (Pub: Powdene Publicity 1998)
- Memories of the LNER: Rural Northumberland by Allan W. Stobbs (Pub: Author 2nd Edition 1992)
- The Newcastle & Carlisle Railway by G Whittle (Pub: David & Charles 1979)
Railway Passenger Stations by M E Quick (Pub: RCHS 2000)
- Clinker’s Register of Closed Passenger Stations and Goods Depots by C R Clinker (Pub: Avon Anglia 1978)
To see other stations on the North Wylam loop line click on the station name: Prudhoe, North Wylam, Newburn, Lemington & Scotswood |

wall_old4.jpg)

wall_old2.jpg)
 Home Page
Home Page 


wall_old3.jpg)






