|
Notes: Thorner station was ideally placed to serve Thorner village which was immediately south of the station. It also served the village of Scarcroft, a mile to the west, and when the station opened it was called Thorner & Scarcroft. In 1885 it was called Scarcroft for a short period before reverting to Thorner & Scarcroft. The name was shortened to Thorner on 1 May 1901.
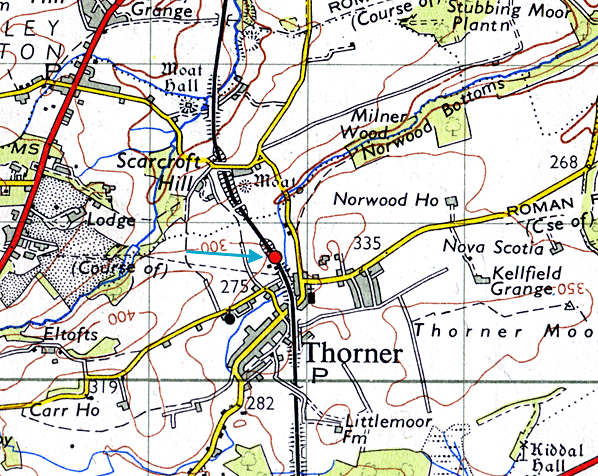
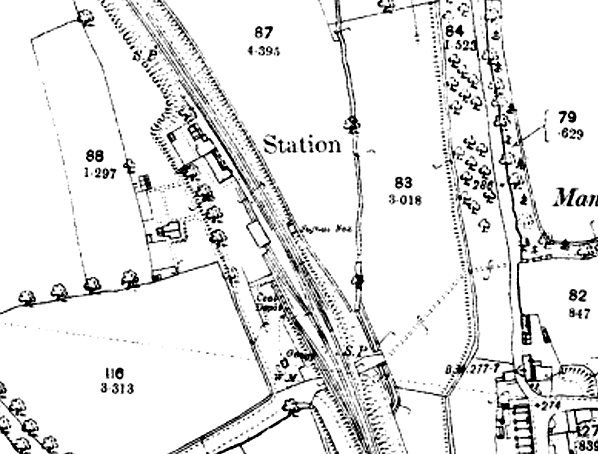
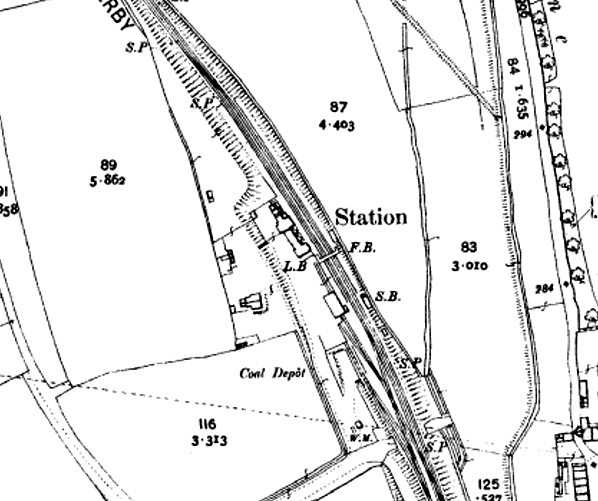
 As built, the station had a single platform with the building on the down side of the line. This was a substantial brick-built structure of a type which is still found at Garforth, about seven miles south, and was similar to a number of other stations scattered around the former NER system, including its neighbours at Collingham Bridge, Bardsey and Scholes. The long office range ended with a single-storey cross-wing; its gable-end on the platform elevation was embellished by frilly bargeboards and it had a bay window with its own gable, with bargeboards to match those of the gable-end. At the opposite, south-eastern, end of the office range was the two-storey station house, projecting on the platform elevation. A verandah supported by two plain columns stretched between the station house and the single-storey cross-wing As built, the station had a single platform with the building on the down side of the line. This was a substantial brick-built structure of a type which is still found at Garforth, about seven miles south, and was similar to a number of other stations scattered around the former NER system, including its neighbours at Collingham Bridge, Bardsey and Scholes. The long office range ended with a single-storey cross-wing; its gable-end on the platform elevation was embellished by frilly bargeboards and it had a bay window with its own gable, with bargeboards to match those of the gable-end. At the opposite, south-eastern, end of the office range was the two-storey station house, projecting on the platform elevation. A verandah supported by two plain columns stretched between the station house and the single-storey cross-wing
There was a long siding opposite the platform but no passing loop. The goods yard was south of the station on the down side. This comprised a loop from which three sidings ran diagonally across the yard. Two of them ran parallel serving a cattle dock, the other running through a brick goods shed to terminate behind the down platform. The other siding, which also had a loop, served coal drops. There was also a two-ton capacity yard crane. Access to the yard was controlled by a signal box on the up side of the long siding opposite the goods shed. The line from Cross Gates was doubled in 1901, and a second platform with a standard NER design timber waiting roof with a sloping roof was provided. A metal footbridge, not of the standard NER pattern, at the south end of the station connected the platforms. The original signal box was retained, and the layout of the goods yard remained unaltered.
In 1911 the station had a catchment area with a population of 2,889. In that year 21,617 tickets were sold, and the main freight handled was barley (327 tons) and potatoes (124 tons) whilst 36 wagons of livestock were loaded at the station.
To encourage standards of maintenance, annual competitions were introduced in 1895 for the ‘best-kept wayside station', and the NER awarded Thorner first prize in 1912 and 1913.
There was no real evidence of modernisation of the station in its British Railways years, and when it closed to passenger and goods traffic from 6 January 1964, it remained oil lit and retained pre-Nationalisation signage. The station and goods yard were cleared for new housing in the 1970s although the platform edges can still be seen in one of the gardens.
BRIEF HISTORY OF THE CHURCH FENTON - HARROGATE RAILWAY & THE CROSS GARES TO WETHERBY RAILWAY
Notes: Harrogate was known as 'The English Spa' in the Georgian era, after its mineral-rich waters were discovered in the sixteenth century. In the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries the chalybeate waters (containing iron) were a popular health treatment, and the influx of wealthy, but sickly, visitors contributed significantly to the wealth of the town.
With the country in the grip of 'railway mania' in the 1840s Harrogate was an obvious target for railway entrepreneurs who were eager to cash in on the town’s popularity, with its wealthy clientele able to pay high fares. In Harrogate local townsfolk and businesses initially opposed the railway, fearing that an influx of people from Leeds and Bradford would lower the tone of the area; but this opposition was overcome. It was going to be a race to see who would be first to reach the town.
The Great North of England Railway (GNER) made the first proposal. Having opened their main line between York and Darlington in 1841 they proposed a branch from Pilmoor, 16 miles north of York, to Harrogate via Boroughbridge and Ripon.
The York & North Midland Railway (Y&NMR) opened in 1839, connecting York with the Leeds & Selby Railway and, in 1840, with the North Midland Railway at Normanton near Leeds. The line was largely financed by ‘Railway King’ George Hudson who invested a substantial inheritance in the North Midland, becoming a director. He then took an active part in the promotion of the route and commissioned George Stephenson to construct the line. Having completed the York line, George Hudson then turned his attention to Harrogate, proposing a branch to the town from a junction with the Y & NM at Church Fenton, ten miles south of York.
The final player was the Leeds & Thirsk Railway (L &TR) who had an ambitious scheme for a new main line linking the industrial regions around Leeds with the north-east. George Hudson had an interest in this scheme as well.
George Hudson was clearly keen to increase the size of his empire, and by 1845 he had taken a lease on the GNER, and he immediately withdrew the Pilmoor - Harrogate proposal to leave the way clear for the two other routes.
 The Y&NMR obtained their Act for the Church Fenton - Harrogate line in 1845, and the eighteen-mile route was staked out in September of that year. It was opened in two stages, with the first 13-mile section between Church Fenton and a temporary terminus at Spofforth opening on 10 August 1847. There were intermediate stations at Stutton, Tadcaster, Newton Kyme, Thorp Arch and Wetherby, with passengers being conveyed the last five miles into Harrogate by horse-drawn omnibus. The only engineering feature of note was a two-span iron girder bridge over the River Wharfe between Newton Kyme and Thorp Arch. The Y&NMR obtained their Act for the Church Fenton - Harrogate line in 1845, and the eighteen-mile route was staked out in September of that year. It was opened in two stages, with the first 13-mile section between Church Fenton and a temporary terminus at Spofforth opening on 10 August 1847. There were intermediate stations at Stutton, Tadcaster, Newton Kyme, Thorp Arch and Wetherby, with passengers being conveyed the last five miles into Harrogate by horse-drawn omnibus. The only engineering feature of note was a two-span iron girder bridge over the River Wharfe between Newton Kyme and Thorp Arch.
The shorter five-mile section between Spofforth and Harrogate took a further year to complete owing to much more difficult terrain, with a gradient of 1 in 36 taking the line up to the unusually narrow 825yd Prospect Tunnel in which trains were not permitted to pass; then 300yd from the tunnel portal, the line crossed the 624yd, 31-arch, Crimple Viaduct which towered 110ft above the valley floor at its highest point. Beyond the viaduct the line went through the 400yd Brunswick Tunnel before entering the terminus at Harrogate Brunswick. (This was the official name of the station, although in timetables it was shown only as Harrogate). The extension to Harrogate opened, without prior announcement or ceremony, on 20 July 1848.
The initial service was five trains per day in each direction with no trains on Sunday. Within two years this had been reduced to three trains each day, probably owing to the opening of the Leeds & Thirsk Railway just five weeks later on 1 September 1848; their station was 1¾ miles to the east at Starbeck. When completed in July 1849, this line provided a more direct route to Leeds without the need to change at Church Fenton. The L&TR had planned to extend their line into Harrogate, but this had to be shelved because of the higher than expected cost of completing their line between Leeds and Starbeck.
In an attempt to prevent competitors from encroaching on its territory, a direct Leeds to York railway was promoted by George Hudson through the Y&NMR. The construction of the line was authorised in 1846 and was to run from Copmanthorpe on the outskirts of York to Cross Gates, several miles east of Leeds, joining the Church Fenton to Harrogate line between Tadcaster and Stutton.
In 1849 George Hudson was forced to resign as chairman of the York & North Midland Railway following his involvement in dubious business activities. The collapse of railway investment in 1849 resulted in the abandonment of the project, but a ten-arch stone viaduct over the River Wharfe at Tadcaster had already been constructed. The need for the line evaporated with the opening of the Micklethorpe to Church Fenton line in 1869 although the viaduct did eventually see rail traffic in the form of a siding serving a flour mill on the east side of the river. The siding closed in 1955. The viaduct is Grade II listed and is owned by Tadcaster Town Council; it now carries a public footpath and cycleway.
The L&TR was renamed the Leeds Northern Railway in 1851, and it was joined by the East and West Yorkshire Junction Railway from York at Knaresborough, east of Harrogate. In 1854 the York & North Midland Railway amalgamated with the Leeds Northern Railway and the York, Newcastle & Berwick Railway to form the North Eastern Railway (NER) which brought control of all the railways in the region under one company. The fledgling NER was quick to improve the railway layout around Harrogate.
The NER built a spur from the former L&TR line at Pannal to join the Y & NMR line west of Prospect Tunnel. Just short of Brunswick Tunnel another new line was built to join the line from Starbeck enabling trains to run into a new central station which opened on 1 August 1862. Brunswick station was closed; initially it was retained for goods traffic, but this was short-lived. By 1880 the service between Harrogate and Church Fenton was restored to five trains per day.
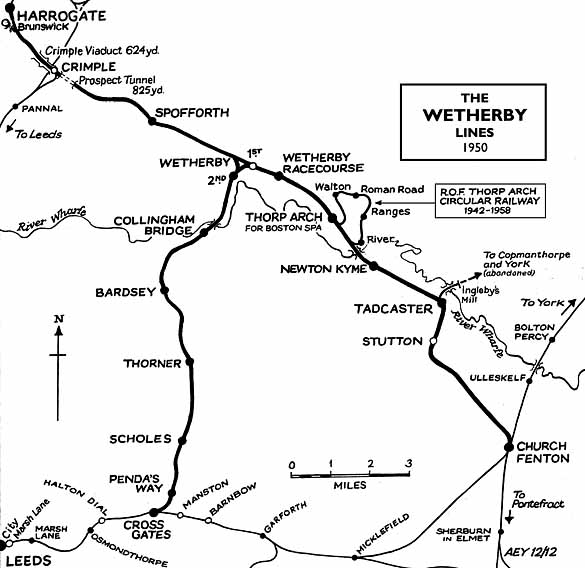 |
The North Eastern Railway soon had plans for other new lines in the region. One of the most ambitious was for a direct route between Leeds and Scarborough by-passing York. For much of its route it would utilise existing lines, but it included new construction from Cross Gates to a junction with the Church Fenton - Harrogate line at Wetherby. On 5 May 1866 The York Herald reported that the Leeds - Wetherby Railway Bill had been put before the Select Committee of the House of Commons for a single line to run from the Leeds and Selby branch, near Cross Gates, to the Church Fenton and Harrogate Branch at Wetherby - a length of 10 miles 66 chains. New capital to be raised was £210,000, with borrowing power of £70,000. The work was to be completed in five years, under penalty. Tenders for the project were invited in November 1871 and seven firms responded with bids.
The Leeds to Scarborough line was eventually abandoned owing to the economic downturn, although some sections were completed including the Cross Gates - Wetherby line which opened on 1 May 1876 with intermediate stations at Scholes, Thorner, Bardsey and Collingham Bridge. The junction at Wetherby faced Church Fenton so it was not possible to run trains into Harrogate. This was rectified in 1901 when the line was doubled and a new curve facing Harrogate was built at Wetherby.
Cross Gates - Harrogate now became an important alternative route to the L&TR which was used increasingly by goods traffic and by the recently introduced Liverpool to Newcastle passenger expresses, which we now able to avoid a reversal at Leeds. As this route by-passed Wetherby station, which was sited to the east of the town, a new Wetherby station opened on 1 July 1902 at the south end of the new triangular junction, with the old station being retained for goods.
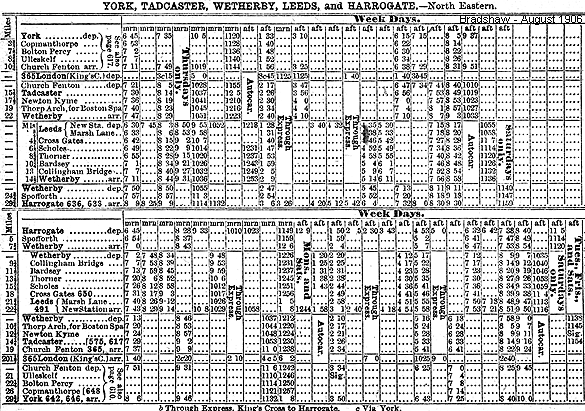
 In 1902 the Great Northern Railway started running express services from Kings Cross to Harrogate via the Church Fenton to Harrogate line, with three daily trains in each direction. These continued after the grouping in 1923 and included the prestigious 'Harrogate Pullman'. Although the Cross Gates to Harrogate line was always considered the major route, the August 1906 timetable shows a good service on both lines with a mixture of stopping and express services. Express trains from London over the Church Fenton - Wetherby line had stopped running by 1947. In 1902 the Great Northern Railway started running express services from Kings Cross to Harrogate via the Church Fenton to Harrogate line, with three daily trains in each direction. These continued after the grouping in 1923 and included the prestigious 'Harrogate Pullman'. Although the Cross Gates to Harrogate line was always considered the major route, the August 1906 timetable shows a good service on both lines with a mixture of stopping and express services. Express trains from London over the Church Fenton - Wetherby line had stopped running by 1947.
Wetherby racecourse opened in 1891, and an untimetabed station was opened c1924 to serve it. This was last used on 18 May 1959, but racecourse specials continued to run to Wetherby station from Bradford Exchange on race days until 1963. A new station called Penda's Way, between Scholes and Cross Gates, was opened on 5 June 1939 to serve the growing residential development in that area.
In March 1940, additional traffic came to the Church Fenton to Wetherby line when a Royal Ordnance Factory was opened at Thorp Arch just to the north of the station. It was constructed for the Ministry of Supply and built on a 450 acre site. It took 18 months to build and cost £5.9 million. Thorp Arch was considered to be an ideal site, away from the large centres of population, possessing a reliable water supply, good rail links and proximity to the A1 trunk road. Workers were brought in from Leeds, Selby, York and all surrounding areas. 10,000 people, mainly women, were employed there at the height of production, and it is believed to have had 619 buildings. In World War II it produced light and medium gun ammunition, heavy ammunition, mines and trench mortar ammunition for the Army; medium and large bombs for the RAF; and 20mm and other small arms ammunition for all three services.
It was linked to the London & North Eastern Railway, which was used in its construction, for supplying raw materials and for transporting away filled munitions. The factory was served by a 6½-mile single-track circular railway with four platforms for munitions workers: these were named River, Ranges, Roman Road and Walton. Special workmen's trains ran from Leeds and Bradford Exchange and from as far afield as Hull and Doncaster on Monday to Saturday calling at the four halts. The last passenger traffic was in 1957 when the five unadvertised trains were withdrawn.
 ROF Thorpe Arch closed twice: once after World War II and then finally after the Korean War in April 1958. Once production had halted, the site was gradually de-contaminated. In the early 1960s George Moore, a local businessman, bought most of the site and the development of the area as a trading estate began. The estate was later owned by Thorp Arch Limited Partnership, but is now known as Thorp Arch Estate and is owned by the trustees of Hanover Property Unit Trust. It comprises an area of over 100 businesses, including the Thorp Arch Retail Park. The most notable addition to the estate is the Northern Reading Room, Northern Listening Service and Document Supply Centre of the British Library, occupying what was the locomotive shed and engineering department. Another part is a prison, originally HMP Thorp Arch, now HMP Wealstun. ROF Thorpe Arch closed twice: once after World War II and then finally after the Korean War in April 1958. Once production had halted, the site was gradually de-contaminated. In the early 1960s George Moore, a local businessman, bought most of the site and the development of the area as a trading estate began. The estate was later owned by Thorp Arch Limited Partnership, but is now known as Thorp Arch Estate and is owned by the trustees of Hanover Property Unit Trust. It comprises an area of over 100 businesses, including the Thorp Arch Retail Park. The most notable addition to the estate is the Northern Reading Room, Northern Listening Service and Document Supply Centre of the British Library, occupying what was the locomotive shed and engineering department. Another part is a prison, originally HMP Thorp Arch, now HMP Wealstun.
Whereas the route between Cross Gates and Harrogate maintained a reasonably frequent weekday service the train frequency via Tadcaster was drastically reduced after WWII. The winter 1937-8 LNER timetable showed 7 trains from Church Fenton to Leeds via Tadcaster on Monday to Friday in each direction, whilst there were twice as many between Leeds, Wetherby and Harrogate. No trains ran on Sunday. The first British Railways (North Eastern Region) timetable of summer 1948 had only three Monday-Friday trains via Tadcaster, but five on Saturday. In summer 1950 only three trains to Leeds and two to Church Fenton were shown. By 1961 there was only one local morning train between Church Fenton and Leeds via Wetherby, and another, also in the morning, from Leeds to Tadcaster, which ran only as far as Thorp Arch on Saturday. No passenger service was shown from Tadcaster to Church Fenton. By 1963 only the 7.44 am departure from Church Fenton to Leeds was shown in the public timetable, the train actually having run from Leeds via Garforth. It is likely that its principal role was to carry parcels. In 1961 there were four trains between Harrogate and Leeds in each direction, with two additional trains between Wetherby and Leeds and one in the opposite direction. Long distance traffic between Leeds and Newcastle had continued to use the line, but this ended with the completion of the quadrupling of the East Coast main line in 1959. The earlier twenty freight trains between Harrogate and Wetherby (in each direction) had fallen to five by 1960.
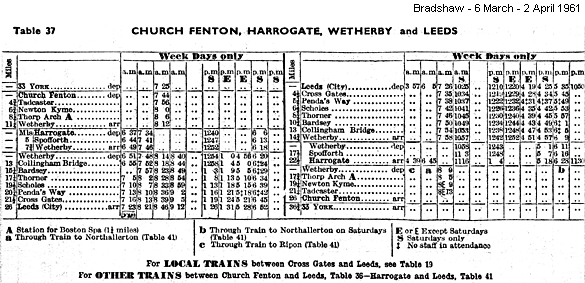 |
In 1961 the recently introduced diesel service between Liverpool and Newcastle was switched from the Arthington route bringing new traffic to the Wetherby line. Although this route was slower it avoided a reversal at Leeds. This renewed importance could not however save the lines. At the time of the Beeching enquiry, there was a maximum of eight passengers on the one train a day between Church Fenton and Leeds via Wetherby, with no regular passengers. There were a few more passengers on the Leeds to Wetherby route but competition from an improving bus service
eventually made passenger numbers unsustainable despite the increase in the number of commuters living in Wetherby. Stations had received minimal investment since Nationalisation, amounting to little more than painting the nameboards in BR(NE) tangerine and installing totem name signs at Wetherby.
Given that all stations were manned, together with sixteen signal boxes and three manually
operated level crossings (requiring 35 staff in total), and the number of steep gradients requiring the use of banking engines, it is of little surprise that it was considered uneconomical. At Wetherby station alone, 14 staff were employed attending to the needs of only 30 passengers per day. The economics of the Wetherby lines were, in fact, worse than the cautionary examples given in Beeching's report. It had a yearly operating cost of £57,000 compared to receipts of £9,000, though some argue that the Wetherby to Leeds route could have been made profitable with some adjustments. Local freight now consisted largely of house coal, the use of which was declining.
 A notable headline at the time read 'First lamb to the Beeching slaughter', cheerfully further stating 'No regular passengers object at inquiry’, which was the case, but only for the Wetherby - Church Fenton line. It was also inaccurate in that the Newcastle – Washington service, earmarked by Beeching, had closed the previous September! A decision was reached on 24 October 1963, the inquiry having taken just three months, with both lines closing to passengers from 6 January 1964. The original Wetherby station remained open for goods traffic until 4 April 1966. The only section of the original route to remain open is the short section of line from the Crimple Viaduct (where the spur from Pannal joined the Church Fenton route to the junction with the line to the former Brunswick terminus. This section is used today by the frequent Leeds – Harrogate – Knaresborough – York services. A new station called Hornbeam Park opened just south of this junction on 24 August 1992. A notable headline at the time read 'First lamb to the Beeching slaughter', cheerfully further stating 'No regular passengers object at inquiry’, which was the case, but only for the Wetherby - Church Fenton line. It was also inaccurate in that the Newcastle – Washington service, earmarked by Beeching, had closed the previous September! A decision was reached on 24 October 1963, the inquiry having taken just three months, with both lines closing to passengers from 6 January 1964. The original Wetherby station remained open for goods traffic until 4 April 1966. The only section of the original route to remain open is the short section of line from the Crimple Viaduct (where the spur from Pannal joined the Church Fenton route to the junction with the line to the former Brunswick terminus. This section is used today by the frequent Leeds – Harrogate – Knaresborough – York services. A new station called Hornbeam Park opened just south of this junction on 24 August 1992.
In the late 1960s, it was evident that Wetherby was going to grow. In 1965 it was estimated that by 1981 the town's population would double to 12,000 and this estimate proved quite accurate. There were ambitious plans to relieve growing congestion through the town centre and on the A58 and A661 by converting the disused railways into relief roads. These suggestions never came to fruition. In Railways around Harrogate, Volume 3 (1998) Martin Bairstow presents a compelling case, headed ‘A lost commuter route?’ for the restoration of passenger services between Leeds and Wetherby. He also remarks that the dieselisation of the service in January 1959 could have increased the use of the trains, but without improved frequency of trains that some neighbouring lines enjoyed, there was really no incentive to use them.
The track was lifted in 1966. Some parts of the former railway tracks between Wetherby and Leeds have been used for housing development at Bardsey and Collingham Bridge. Sustrans National Cycle Network routes 66 and 67 use some of the remaining trackbed. This line is walkable from Cross Gates to a point south of Collingham where a landowner refuses access to a short section of the line. At Scholes muddy conditions are encountered, but this soon gives way to a grassy embankment with lots of sandstone bridges in situ. The most impressive stretch is just north of Thorner where the line passes through a very deep, narrow cutting with the Seacroft road soaring above on a high brick bridge. At Collingham the road bridge must be used to cross the Wharfe, but from the north bank a footpath follows the embankment, sandwiched between a golf course and the river, into Wetherby. A public footpath and cycleway follows the trackbed from the A1 (M) to Thorp Arch station and from Wetherby to Stofforth - this section of the path is known as Harland Way..
Tickets from Michael Stewart. Bradshaws from Nick Catford & Chris Hind . Route map drawn by Alan Young.
Thanks to Martin Bairstow (author/publisher), Peter Tuffrey (author) and the Wetherby Historical Trust who supplied many of the photos used in this feature.
Sources:
To see other stations on the Harrogate - Church Fenton line
click on the station name:
Harrogate Brunswick, Hornbeam Park, Crimple, Spofforth, Wetherby (1st site), Wetherby Racecourse, Thorp Arch, Newton Kyme, Tadcaster,
Stutton & Church Fenton
See also River Platform, Ranges Platform, Roman Road Platform &
Walton Platform on the ROF Thorp Arch Militery Railway.
Special feature: Royal Ordnance Factory 8 - Thorp Arch
To see stations on the Cross Gates - Wetherby line click on the station name: Cross Gates, Penda's Way, Scholes, Bardsey, Collingham Bridge
and Wetherby (2nd site)
|

old1.jpg)
old2.jpg)
old4.jpg) Station staff pose in front of the main station building at Thorner c1907.
Station staff pose in front of the main station building at Thorner c1907.old3.jpg)
old4.jpg)
old8.jpg)
old8.jpg)
old5.jpg)
old6.jpg)
1.jpg)
1.jpg)
6.jpg)
 As built, the station had a single platform with the building on the down side of the line. This was a substantial brick-built structure of a type which is still found at Garforth, about seven miles south, and was similar to a number of other stations scattered around the former NER system, including its neighbours at Collingham Bridge, Bardsey and Scholes. The long office range ended with a single-storey cross-wing; its gable-end on the platform elevation was embellished by frilly bargeboards and it had a bay window with its own gable, with bargeboards to match those of the gable-end. At the opposite, south-eastern, end of the office range was the two-storey station house, projecting on the platform elevation. A verandah supported by two plain columns stretched between the station house and the single-storey cross-wing
As built, the station had a single platform with the building on the down side of the line. This was a substantial brick-built structure of a type which is still found at Garforth, about seven miles south, and was similar to a number of other stations scattered around the former NER system, including its neighbours at Collingham Bridge, Bardsey and Scholes. The long office range ended with a single-storey cross-wing; its gable-end on the platform elevation was embellished by frilly bargeboards and it had a bay window with its own gable, with bargeboards to match those of the gable-end. At the opposite, south-eastern, end of the office range was the two-storey station house, projecting on the platform elevation. A verandah supported by two plain columns stretched between the station house and the single-storey cross-wing
 The Y&NMR obtained their Act for the Church Fenton - Harrogate line in 1845, and the eighteen-mile route was staked out in September of that year. It was opened in two stages, with the first 13-mile section between Church Fenton and a temporary terminus at Spofforth opening on 10 August 1847. There were intermediate stations at Stutton, Tadcaster, Newton Kyme, Thorp Arch and Wetherby, with passengers being conveyed the last five miles into Harrogate by horse-drawn omnibus. The only engineering feature of note was a two-span iron girder bridge over the River Wharfe between Newton Kyme and Thorp Arch.
The Y&NMR obtained their Act for the Church Fenton - Harrogate line in 1845, and the eighteen-mile route was staked out in September of that year. It was opened in two stages, with the first 13-mile section between Church Fenton and a temporary terminus at Spofforth opening on 10 August 1847. There were intermediate stations at Stutton, Tadcaster, Newton Kyme, Thorp Arch and Wetherby, with passengers being conveyed the last five miles into Harrogate by horse-drawn omnibus. The only engineering feature of note was a two-span iron girder bridge over the River Wharfe between Newton Kyme and Thorp Arch.
 In 1902 the Great Northern Railway started running express services from Kings Cross to Harrogate via the Church Fenton to Harrogate line, with three daily trains in each direction. These continued after the grouping in 1923 and included the prestigious 'Harrogate Pullman'. Although the Cross Gates to Harrogate line was always considered the major route, the August 1906 timetable shows a good service on both lines with a mixture of stopping and express services. Express trains from London over the Church Fenton - Wetherby line had stopped running by 1947.
In 1902 the Great Northern Railway started running express services from Kings Cross to Harrogate via the Church Fenton to Harrogate line, with three daily trains in each direction. These continued after the grouping in 1923 and included the prestigious 'Harrogate Pullman'. Although the Cross Gates to Harrogate line was always considered the major route, the August 1906 timetable shows a good service on both lines with a mixture of stopping and express services. Express trains from London over the Church Fenton - Wetherby line had stopped running by 1947.
 ROF Thorpe Arch closed twice: once after World War II and then finally after the Korean War in April 1958. Once production had halted, the site was gradually de-contaminated. In the early 1960s George Moore, a local businessman, bought most of the site and the development of the area as a trading estate began. The estate was later owned by Thorp Arch Limited Partnership, but is now known as Thorp Arch Estate and is owned by the trustees of Hanover Property Unit Trust. It comprises an area of over 100 businesses, including the Thorp Arch Retail Park. The most notable addition to the estate is the Northern Reading Room, Northern Listening Service and Document Supply Centre of the British Library, occupying what was the locomotive shed and engineering department. Another part is a prison, originally HMP Thorp Arch, now HMP Wealstun.
ROF Thorpe Arch closed twice: once after World War II and then finally after the Korean War in April 1958. Once production had halted, the site was gradually de-contaminated. In the early 1960s George Moore, a local businessman, bought most of the site and the development of the area as a trading estate began. The estate was later owned by Thorp Arch Limited Partnership, but is now known as Thorp Arch Estate and is owned by the trustees of Hanover Property Unit Trust. It comprises an area of over 100 businesses, including the Thorp Arch Retail Park. The most notable addition to the estate is the Northern Reading Room, Northern Listening Service and Document Supply Centre of the British Library, occupying what was the locomotive shed and engineering department. Another part is a prison, originally HMP Thorp Arch, now HMP Wealstun.

 A notable headline at the time read 'First lamb to the Beeching slaughter', cheerfully further stating 'No regular passengers object at inquiry’, which was the case, but only for the Wetherby - Church Fenton line. It was also inaccurate in that the Newcastle – Washington service, earmarked by Beeching, had closed the previous September! A decision was reached on 24 October 1963, the inquiry having taken just three months, with both lines closing to passengers from 6 January 1964. The original Wetherby station remained open for goods traffic until 4 April 1966. The only section of the original route to remain open is the short section of line from the Crimple Viaduct (where the spur from Pannal joined the Church Fenton route to the junction with the line to the former Brunswick terminus. This section is used today by the frequent Leeds – Harrogate – Knaresborough – York services. A new station called Hornbeam Park opened just south of this junction on 24 August 1992.
A notable headline at the time read 'First lamb to the Beeching slaughter', cheerfully further stating 'No regular passengers object at inquiry’, which was the case, but only for the Wetherby - Church Fenton line. It was also inaccurate in that the Newcastle – Washington service, earmarked by Beeching, had closed the previous September! A decision was reached on 24 October 1963, the inquiry having taken just three months, with both lines closing to passengers from 6 January 1964. The original Wetherby station remained open for goods traffic until 4 April 1966. The only section of the original route to remain open is the short section of line from the Crimple Viaduct (where the spur from Pannal joined the Church Fenton route to the junction with the line to the former Brunswick terminus. This section is used today by the frequent Leeds – Harrogate – Knaresborough – York services. A new station called Hornbeam Park opened just south of this junction on 24 August 1992.
old_thumb9.jpg)
old_thumb7.jpg)
thumb2.jpg)
thumb3.jpg)
thumb7.jpg)
thumb8.jpg)
thumb4.jpg)
thumb5.jpg)
thumb9.jpg)
thumb10.jpg)
thumb11.jpg)

 Home Page
Home Page